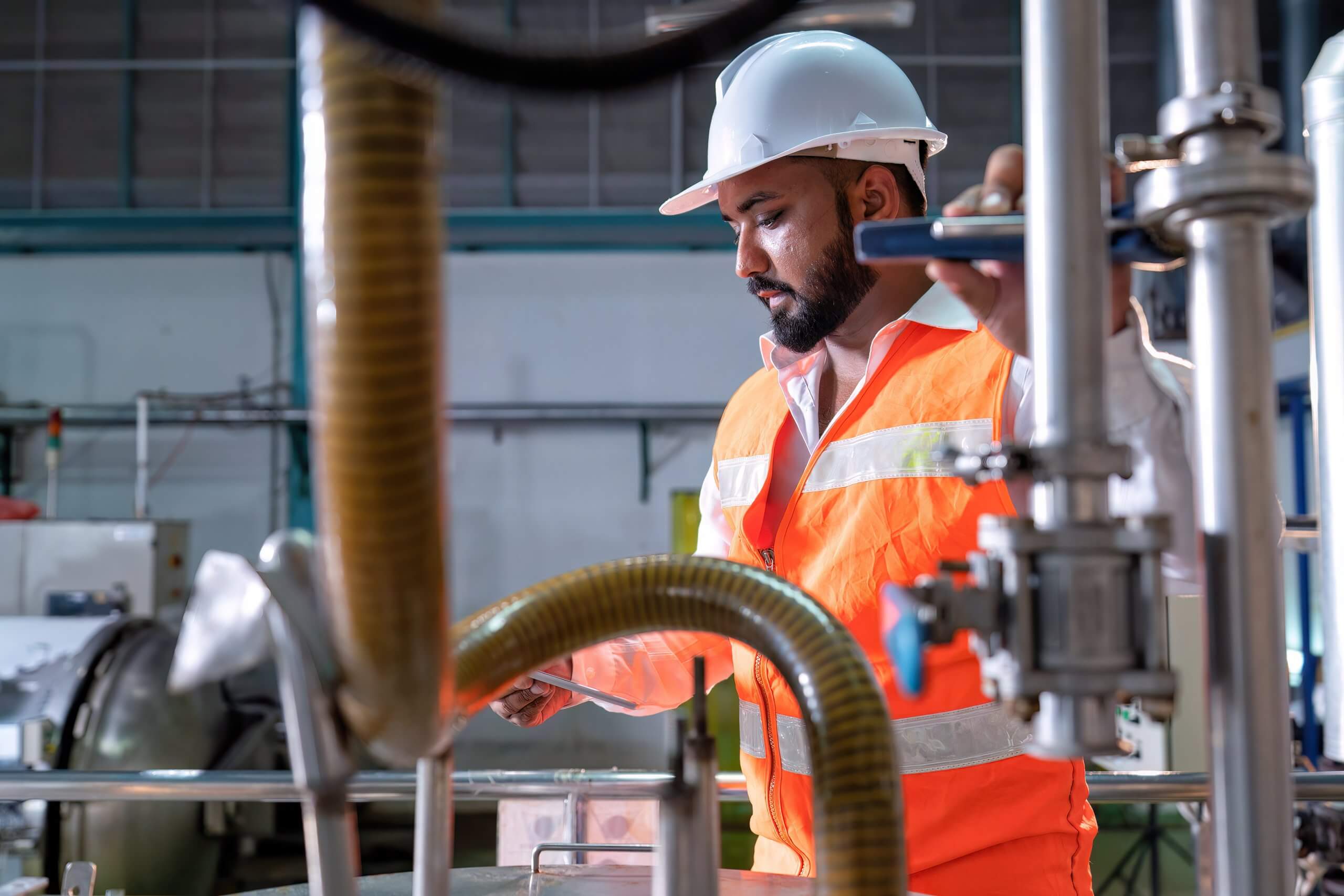
ACHIEVE WHAT'S POSSIBLE WITH KEFMANN
About Kefmann
At Kefmann, our commitment revolves around delivering top-tier chemical products tailored to the distinct requirements of our clients. Over the years, we’ve prioritized not only enhancing the quality of our products but also refining the service we extend to clients globally. With extensive knowledge and experience in the chemical industry, we actively pursue and incorporate the latest technologies and innovations into our production processes. What sets us apart from the competition is our unwavering passion for the success of our clients.
Worldwide Supply Network
With our Worldwide Supply Network, we effortlessly source, produce, and distribute products globally, connecting seamlessly with suppliers and distributors worldwide.
Supply Partner
Kefmann is an excellent supply partner, contributing effectively to the supply chain and ensuring seamless connections with suppliers and distributors worldwide.
Logistic Solutions
With our Worldwide Supply Network, we effortlessly source, produce, and distribute products globally, ensuring seamless connections with suppliers and distributors worldwide.
Sourcing
We are continually collaborating with a wide variety of suppliers to meet our clients’ diverse needs, ensuring efficient and seamless service across every aspect of the supply chain.
Our Commitments
Lorem ipsum dolor consectetur adipiscing tempor incididunt labore dolore magna aliqua pellentesque gravida natoque penatibus magnis.
- Wide Range of Products
- Product Avaliablity
- Logistic Solitions for Client Needs
- Wide Range of Supliers
- Avaliability
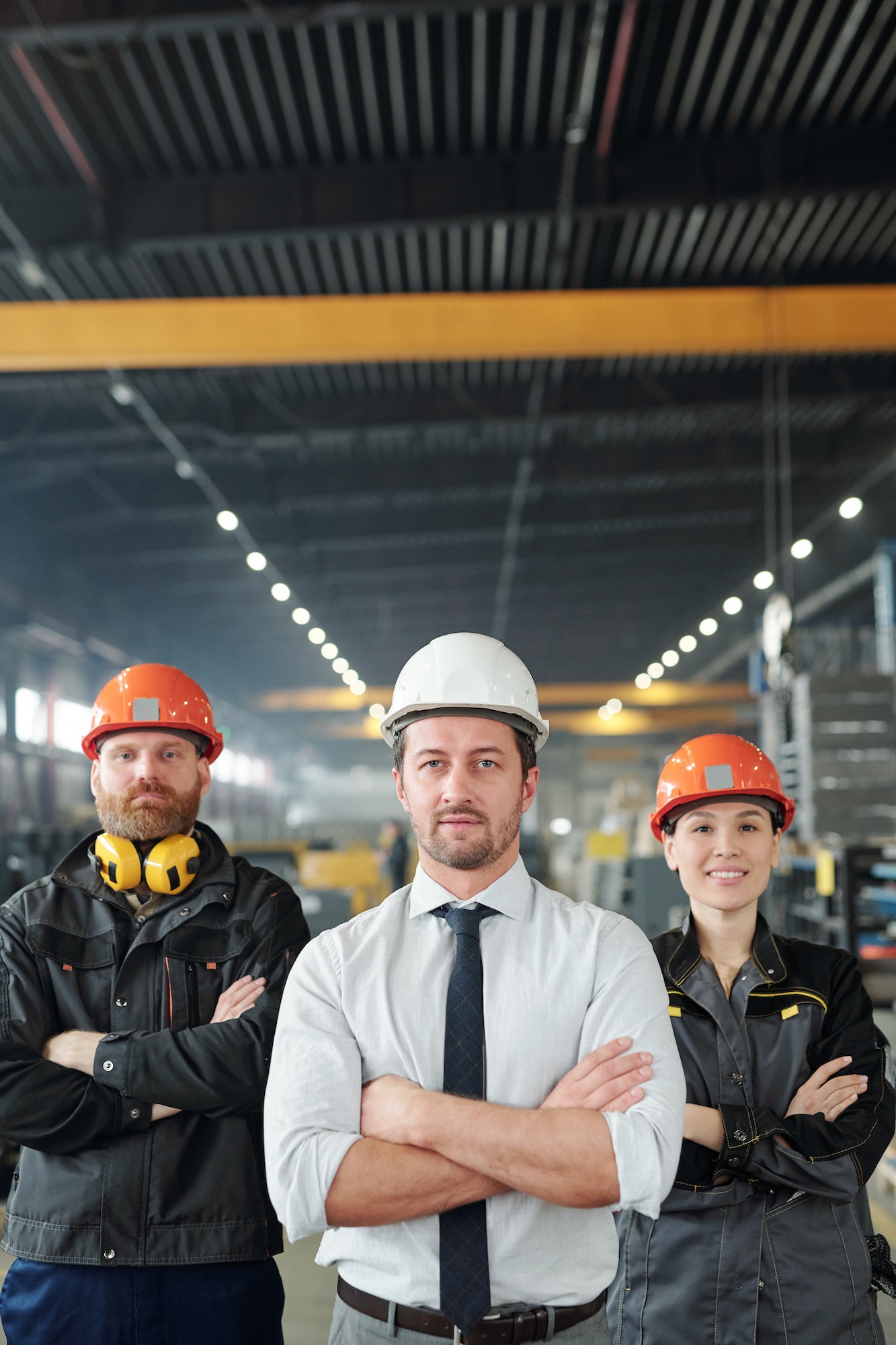

YEAR EXPERIENCE
SUCCESFUL PROJECTS
HAPPY CLIENT
INNOVATIVE SOLUTIONS FROM THE CHEMICAL INDUSTRY
Ecological Production
Environmentally friendly production with sustainable and eco-conscious chemical processes.
Chemical Processing Industry
Innovative solutions for the processing and production of chemical substances and compounds.

Renewable Energy Chemicals
Chemical solutions and products specifically designed for renewable energy sources.

Petrochemical Industry
Production and development of chemical products derived from oil and natural gas.
Nuclear Chemistry
Development of chemicals and processes required for nuclear energy production.
Wood Processing Chemicals
Chemical solutions used in wood processing and preservation processes.
OUR STEPS COOPERATION IN BUSINESS
Lorem ipsum dolor consectetur adipiscing tempor incididunt labore dolore
01
Preparation of Project Documents
Identifying customer needs and preparing necessary documentation for chemical products.
02
Creation of a Project and On-Time Delivery
Developing chemical solutions and products with our expert team based on project requirements.
03
Completion of the Project and Payment
Finalizing the delivery of products and completing the payment process following customer satisfaction.
04
Maintenance of Products
Providing quick and effective maintenance services for any issues with chemical products and machinery.


